Direct Drive vs Bowden Extruder: What to Choose?
Introduction
Hey there! Welcome to the world of 3D printing, a fascinating realm where your ideas can literally take shape before your eyes. At the heart of this exciting world are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers. Imagine a hot glue gun crossed with a computer-controlled robot – that's kind of what these printers are like. They melt plastic, then precisely lay it down layer by layer to create an object. It's like magic, but it's science!
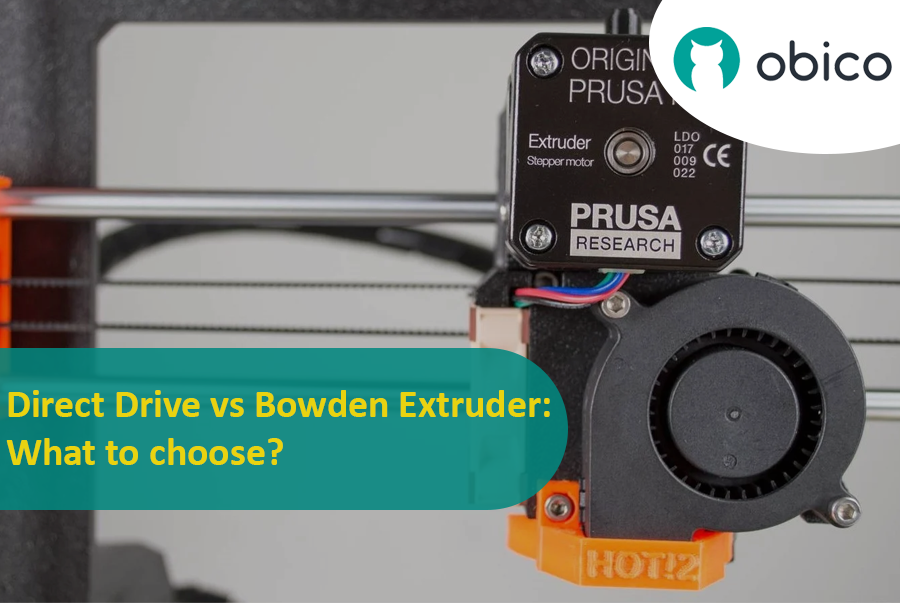
Now, let's talk about a crucial part of these printers: the extruders. Think of an extruder as the 'hand' of the printer that does the actual work of laying down the melted filament. It's a key player because how well your 3D printer can extrude filament determines the quality of your print. Good extrusion means smooth, detailed prints; poor extrusion can lead to a whole host of problems.
There are two main types of extruders you'll hear about: Direct Drive and Bowden. Each has its own set of fans and its own unique strengths and weaknesses. In this guide, we'll dive into the world of these extruders, compare them side by side, and help you figure out which one might be the best fit for your 3D printing adventures. So, let's get started!
Understanding the Extruders
Alright, let's get to know our two key players in the 3D printing game: the Direct Drive and Bowden Extruders. These aren't just fancy names; they represent two fundamentally different approaches to pushing filament through your printer.
Direct Drive Extruder
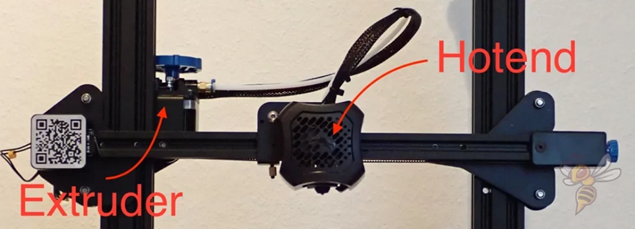
Picture this as the 'straightforward' approach. In a Direct Drive setup, the extruder – which is responsible for feeding filament – is mounted right on top of the printhead. It's like having your pencil sharpener attached directly to your pencil; as you write, you can sharpen it without skipping a beat. This setup allows the filament to move directly into the hotend (the part that melts the filament) with very little distance to travel. It's like a short and direct path from A to B.

Bowden Extruder
Now, imagine a scenario where your pencil sharpener is at the other end of your desk. You have to walk the pencil over to the sharpener every time it gets dull. That's somewhat how a Bowden Extruder works. In this setup, the extruder is mounted separately from the printhead, usually on the frame of the printer. The filament travels from the extruder to the printhead through a long tube, known as the Bowden tube. It's like a mini filament highway, allowing the printhead to move more freely since it's not weighed down by the extruder.
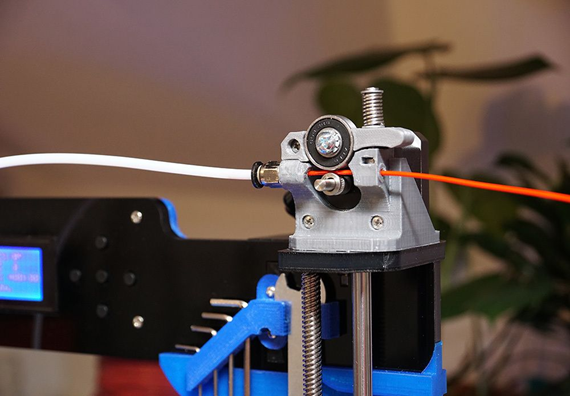
Both of these systems have the same goal: to smoothly and accurately feed filament for printing. However, the way they achieve this goal differs, and these differences impact the printer's performance in various ways. The Direct Drive system is all about proximity and precision, while the Bowden system focuses on lightness and mobility. As we explore further, you'll see how these characteristics play out in the real world of 3D printing. Stay tuned!
Direct Drive Extruder
Definition and Structure
Let's get up close and personal with the Direct Drive Extruder. Imagine a relay race where the baton is passed directly from one runner to the next, without any detours. That's pretty much how a Direct Drive Extruder operates in the 3D printing world. It's mounted right on the printhead, and its job is to grab the filament and feed it straight into the hotend, which is just a stone's throw away. This close-knit arrangement means the filament doesn't have to travel far, reducing the chance of it getting sidetracked or lost along the way.
Advantages
Reliable Extrusion: Because the filament's journey from extruder to hotend is so short, there's less room for error. This results in more consistent and reliable extrusion, which is a big deal in getting those prints just right.
Better Retraction: Imagine you're sipping a beverage through a short straw; you can control the flow easily. Similarly, in a Direct Drive system, the extruder can quickly and effectively retract the filament, helping reduce issues like oozing or stringing that can occur between print sections.
Wide Range of Filaments: These guys are not picky eaters. Direct Drive Extruders can handle a variety of filaments, from the flexible and finicky ones to the tough and abrasive types. This flexibility opens up a world of possibilities for your printing projects.
Disadvantages
Heavier Printhead: However, it's not all smooth sailing. With the extruder sitting on the printhead, it's like carrying a backpack on a hike – it adds weight. This extra load can slow down print speeds and affect the printer's ability to quickly and accurately move in the X and Y directions.
Maintenance Challenges: When it's time for a tune-up or a fix, the Direct Drive setup can be a bit of a headache. Since everything is packed into the printhead, accessing certain parts for maintenance or cleaning can be more fiddly compared to a Bowden setup.
Bowden Extruder
Definition and Structure
Welcome to the realm of the Bowden Extruder, where things are a bit more... distant. Picture this: rather than having everything bundled together like in the Direct Drive setup, the Bowden Extruder takes a more long-distance approach. Here, the extruder isn't mounted on the printhead but is instead attached to the frame of the printer. It sends the filament on a journey through a PTFE tube (fondly known as the Bowden tube) to reach the hotend at the printhead. It's like having a supply line running from your pencil case to your pencil; a bit more complex, but it has its perks.
Advantages
Cleaner Movements: The reduced weight on the printhead, thanks to the extruder being mounted on the printer's frame, allows for more agile and precise movements. This can often translate to cleaner prints, particularly in high-speed printing scenarios where the lighter printhead can more easily handle quick directional changes.
Potential for a More Streamlined Printhead Design: While a Bowden setup does not inherently increase the printer's build volume, it can allow for a more compact and streamlined printhead design. This is because the extruder, which is one of the heavier components, is not mounted on the printhead itself. In some printer designs, this might contribute to a more optimized use of the printer’s existing build space, especially in terms of the printhead’s ability to navigate and access the entire build area more efficiently.
Disadvantages
More Powerful Motor Required: Life's not always easy on the Bowden side. The longer distance and the friction inside the tube mean the extruder needs to work harder to push and pull the filament. This calls for a more robust motor with more torque.
Slower Response Time: Think of trying to communicate over a longer distance – it takes time. Similarly, the Bowden setup, with its longer filament path, can lead to a lag in response time. This can be noticeable when it comes to starting and stopping the flow of filament, which is critical for quality printing. It requires faster retraction settings to avoid issues like stringing.
Comparative Analysis
Now that we're acquainted with both Direct Drive and Bowden Extruders, let's put them side by side and see how they measure up in different aspects.
Performance with Different Filaments
Direct Drive Extruder: This setup is like a versatile chef; it can handle a wide variety of filament "recipes" with ease. From the standard PLA and ABS to the more challenging flexible and abrasive materials, the Direct Drive is adept at managing them all. Its short path and direct control over the filament make it particularly good at printing with soft and flexible filaments, which might otherwise buckle or jam in longer tubing.
Bowden Extruder: Think of the Bowden as more of a specialist in rigid materials. It's great with standard filaments like PLA and ABS but can struggle with the softer, more flexible types. The longer path and potential for filament bending or compression make it less ideal for materials like TPU, where precision and control are key.
Impact on Printing Speed and Quality
Direct Drive Extruder: It's steady and precise, but not the fastest runner due to the added weight on the printhead. This can lead to slower movement, affecting overall print speed. However, the proximity of the extruder to the nozzle allows for better control, which can result in higher print quality, especially with complex prints or those requiring a lot of retractions.
Bowden Extruder: Light on its feet, the Bowden setup allows for faster printhead movement, potentially leading to quicker print times. However, the trade-off comes in the form of a slightly reduced control over filament extrusion, which might affect print quality, particularly with intricate designs or where fine detail is required.
Maintenance and Durability
Direct Drive Extruder: Maintenance can be a bit more hands-on due to the complexity of having the extruder mounted on the printhead. Accessing certain parts for cleaning or replacement might require a bit more effort. However, its straightforward design often means fewer points of failure, which can be a plus for long-term durability.
Bowden Extruder: Generally, the Bowden setup is easier to maintain since the extruder is mounted on the frame and not on the moving printhead. However, the Bowden tube itself might need regular replacement, especially if printing with abrasive materials. The longer filament path can also introduce additional wear points.
Choosing the Right Extruder for Your Needs
Selecting the right extruder for your 3D printer is a bit like choosing the right pair of shoes – it all depends on where you're going and what you'll be doing. Let's walk through some key considerations and application-specific recommendations to help you make the best choice for your 3D printing journey.
Considerations for Selecting an Extruder
Type of Filaments You Plan to Use: If your projects involve a variety of filaments, especially flexible or abrasive types, a Direct Drive system is your go-to. It handles these materials with greater ease and precision. For standard filaments like PLA or ABS, a Bowden setup will do just fine.
Desired Print Quality vs. Speed: If you're all about detail and precision, and don't mind a slower pace, Direct Drive will be your faithful companion. However, if speed is your need and you're working mostly with simpler designs, the Bowden's light-footed nature makes it a better match.
Printer's Design and Capabilities: Consider the design of your 3D printer. Some printers, especially lightweight or delta-style ones, may not accommodate the additional weight of a Direct Drive extruder efficiently.
Maintenance and Upkeep: Are you okay with a bit more maintenance work? If you prefer simpler upkeep, a Bowden extruder could be more up your alley. Direct Drive systems, while not excessively demanding, do require more frequent attention.
Upgrade Possibilities: If you're considering upgrading your current printer, assess whether it's compatible with the extruder type you're leaning towards. Some printers are easier to modify than others.
Application-Specific Recommendations
- For High Precision and Special Materials: If you're into printing highly detailed models or using materials like TPU (flexible filament), go with a Direct Drive. Its control and precision make it ideal for intricate designs and challenging materials.
- For Speed and Efficiency: If you're more into producing larger quantities, prototypes, or less complex models where speed is essential, a Bowden extruder will serve you well. It's great for educational settings or hobbyists who value efficiency and speed.
- For Beginners: New to the 3D printing world? A Bowden extruder might be a good starting point due to its simplicity and ease of use.
- For Advanced Users and Tinkerers: If you love tweaking and customizing your printer, a Direct Drive offers more flexibility for modifications and experimenting with different materials.
Case Studies and Examples
To bring our discussion into the real world, let's look at some examples of 3D printers that employ either the Direct Drive or Bowden extruder systems. These case studies will illustrate how the choice of extruder can impact actual printing experiences and outcomes.
Direct Drive Extruder Examples
Prusa i3 MK4: Known for its reliability and high-quality prints, the Prusa i3 MK4 is a favorite in the 3D printing community. It uses a Direct Drive system, which allows users to experiment with a wide range of materials, including flexible filaments like TPU. This printer is often praised for its detailed and accurate prints, showcasing the advantages of Direct Drive in achieving high precision.

Creality Ender 3 S1 Pro: Another popular model, the Ender 3 S1 Pro, chooses Direct Drive for its extrusion system. Users of this printer often note the ease of printing with flexible and abrasive materials. The printer demonstrates the robustness and versatility of Direct Drive setups, especially for hobbyists and small businesses that require a wide range of printing capabilities.

Bowden Extruder Examples
Creality Ender 3 V2: A widely recognized and affordable printer, the Ender 3 V2 uses a Bowden setup. This printer is known for its efficiency and speed, making it a great choice for beginners and those focusing on printing with standard materials like PLA and ABS. The lighter printhead results in faster print speeds, ideal for those who prioritize efficiency and volume.

Elegoo’s Neptune 3: This is another example of a 3D printer that employs a Bowden extruder system. Elegoo’s Neptune 3 is designed to leverage the advantages of a Bowden setup, such as a lighter printhead for cleaner and faster movements. This makes it well-suited for projects where speed and efficient printing of standard materials are key considerations.

Real-World Implications
Flexibility vs. Specialization: Direct Drive printers, like the Prusa i3 MK4, offer greater flexibility in materials and print quality, making them ideal for users who require versatility and precision. Bowden printers, like the Ender 3 V2, cater to users who prioritize speed and efficiency with standard materials.
Maintenance and Learning Curve: The Direct Drive systems, while offering greater control, also come with a steeper learning curve and potentially more maintenance. This is evident in printers like the Ender 3 S1 Pro, where users might need to invest more time in upkeep. In contrast, Bowden systems, seen in printers like the Elegoo’s Neptune 3, offer easier maintenance, making them more suitable for beginners or those who prefer a more straightforward experience.
Cost and Upgradability: Generally, Direct Drive printers can be more expensive due to their complex mechanisms. However, they offer more room for upgrades and modifications, as seen in the enthusiast community around the Prusa series. Bowden printers, often being more affordable, provide a cost-effective solution for standard printing needs but might have limitations when it comes to upgrades.
Upgrading and Customization Options
Embarking on an upgrade journey for your 3D printer's extruder system can be both exciting and a bit daunting. Whether you're looking to switch from a Bowden to a Direct Drive system (or vice versa), or you're aiming to enhance the capabilities of your current setup, there are several factors and options to consider. Let's dive into the world of extruder upgrades and customizations!
Upgrading from Bowden to Direct Drive (and Vice Versa)
- Compatibility Check: Before you start, ensure your printer's frame and motor can support the new extruder type. Direct Drive systems are heavier and might require a sturdier frame and a more powerful motor.
- Acquiring the Right Kit: Many manufacturers offer upgrade kits. For instance, if you're upgrading an Ender 3 from Bowden to Direct Drive, Creality and third-party vendors have kits for this purpose.
- Calibration and Firmware Updates: After the physical upgrade, you'll need to recalibrate your printer and possibly update the firmware to accommodate the new extruder type. This includes adjusting steps per millimeter settings for accurate filament feeding.
- Learning Curve: Be prepared for a learning phase, especially if you're switching to a Direct Drive system. You'll need to understand the nuances of handling different filaments and the implications on print speed and quality.
Customization Options for Direct Drive Extruders
- Lightweight Upgrades: Look for lightweight extruder designs to minimize the added weight on the printhead, which can help maintain print speed and reduce wear on the printer.
- Gear Ratio Modifications: Some Direct Drive systems allow you to alter the gear ratio for finer control over filament feeding, which can be particularly useful for detailed prints or specialty filaments.
- Cooling Enhancements: Upgrading the cooling system around the extruder can improve print quality by ensuring optimal operating temperatures, especially for printers that handle high-temperature materials.
Customization Options for Bowden Extruders
- Tube Upgrades: Replacing the standard PTFE tube with a high-quality one can reduce friction and improve filament feeding consistency. Look for tubes with better temperature and wear resistance.
- Extruder Gear Upgrades: Upgrading to a high-quality extruder gear can enhance the precision of filament feeding, which is crucial for a Bowden setup.
- Motor Upgrades: Since Bowden setups benefit from powerful motors, upgrading to a motor with higher torque can improve overall performance, especially when printing at higher speeds.
General Customization Tips
Silent Stepper Drivers: Regardless of the extruder type, upgrading to silent stepper drivers can make your printing process quieter and smoother.
Filament Runout Sensors: Adding a filament runout sensor can save prints from failing due to filament shortages, a handy addition for both Direct Drive and Bowden setups.
FAQs: Direct Drive vs. Bowden Extruders
- What is the main difference between Direct Drive and Bowden Extruders? The main difference lies in their structure and placement. In Direct Drive systems, the extruder is mounted directly on the printhead, pushing filament into the nozzle with a short path. Bowden Extruders have the extruder mounted on the printer's frame, pushing filament through a longer tube to the printhead.
- Can I switch from a Bowden to a Direct Drive system (or vice versa) on my 3D printer? Yes, it's possible to switch between these systems, but it requires compatibility checks, purchasing the right kit, and potentially recalibrating and updating your printer’s firmware.
- Which extruder type is better for printing with flexible filaments? Direct Drive extruders are generally better for printing with flexible filaments due to their precise control and shorter filament path, which reduce the chances of filament buckling or jamming.
- Does a Bowden Extruder improve printing speed? Yes, a Bowden setup can improve print speeds because the printhead is lighter, allowing for faster and more agile movements.
- Are Direct Drive Extruders more difficult to maintain? Direct Drive systems can be more challenging to maintain due to their compact and integrated structure on the printhead, making access to certain parts for cleaning or repairs a bit more intricate.
- Will upgrading to a Direct Drive system improve my print quality? While an upgrade can potentially improve print quality, especially for detailed prints or with challenging materials, it's not a guaranteed solution. Print quality also depends on other factors like printer calibration, filament quality, and print settings.
- Is it necessary to upgrade the motor when switching to a Direct Drive system? It might be necessary, especially if your printer's original motor isn't powerful enough to handle the extra weight and torque requirements of a Direct Drive system.
- Can a Bowden setup handle all types of filaments? While Bowden extruders can handle a variety of filaments, they might struggle with very flexible or soft materials due to the longer filament path that can cause binding or inconsistency in feeding.
- Are there any specific printers that work best with a Direct Drive or Bowden setup? The suitability depends on the printer's design and intended use. Printers like the Prusa i3 series often use Direct Drive for their versatility and precision, while models like the Creality Ender series commonly use Bowden setups for their speed and efficiency.
- What are some common upgrades for Bowden Extruders? Common upgrades include high-quality PTFE tubes, better extruder gears for precise filament feeding, and more powerful motors to handle the extrusion process more effectively.
Conclusion
In the intricate dance of 3D printing, the type of extruder you choose plays a pivotal role in how gracefully your printer performs. Let's recap the key points of our exploration into Direct Drive and Bowden Extruders and offer some final thoughts on making the right choice for your needs.
Direct Drive Extruders
- Close Proximity: The extruder is mounted directly on the printhead, offering a short path for the filament into the nozzle.
- Advantages: Superior control over filament extrusion, better performance with flexible and abrasive materials, and improved retraction capabilities.
- Disadvantages: Added weight on the printhead leads to potential reductions in speed and increased wear, along with potentially more complex maintenance.
Bowden Extruders
- Separate Setup: The extruder is mounted on the printer's frame, pushing filament through a long tube to the printhead.
- Advantages: Lighter printhead resulting in faster printing speeds and potentially larger build volumes.
- Disadvantages: Longer filament path can complicate the use of flexible materials, require a more powerful motor, and result in slower response times in filament retraction.
Choosing the Right Extruder
The decision hinges on what you prioritize in your 3D printing ventures. If precision, control, and versatility with various filament types are your top concerns, a Direct Drive system is your likely ally. On the flip side, if speed, efficiency, and ease of maintenance rank higher on your list, then a Bowden setup might be more up your alley.
In the end, whether you choose a Direct Drive or a Bowden extruder, each has its unique strengths and potential drawbacks. The choice doesn't have to be black and white; it's more about what shades of gray best match your specific printing needs and aspirations. With the right setup, your 3D printing experience can be not just functional, but truly enjoyable and fulfilling.
