Orca Slicer VS PrusaSlicer: Everything You Need To Know
Slicers can make or break your 3D print - quite literally. Over time, there have been many slicers, but two have remained favorites for the 3D printing community—Orca and Prusa.
What happens when you have to choose between these two slicers? Let’s dive straight into it the right way!
What Is a Slicer?
3D printing works layer by layer. Each layer is printed on top of another, and a 3D printing slicer converts your 3D part into 2D layers for the printer to follow and print.
A slicer also sends numerical code which positions the extruder, adjusts layer height, printing parameters, and supports. This makes the choice of slicer important, and switching to a new slicer is often a worthwhile upgrade.
Why Is Orca Slicer So Popular?
Orca slicer is based on Bambu Studio (slicer for Bambu lab printers) and gives the best of both worlds. It’s an enhanced version of Bambu studio based on Prusa slicer with a more user-friendly interface, wide support for printers and regular updates.
The main selling point of the Orca slicer is its multi-printer support. Bambu Studio, which has some of the most advanced slicing features, does not offer compatibility to except a select few, but Orca, based on Bambu, is open-source and brings advanced features to many printers.
It offers a balance of printer settings for beginners and advanced users, and it works well with Klipper-based printers like Ratrig.

Where Prusa Slicer Differentiates
PrusaSlicer is the official slicer for Prusa printers and is highly stable with version upgrades from time to time. Prusa does not add experimental features like Orca and focuses on tested improvements and features that work long-term.
PrusaSlicer offers more control to the user, like allowing you to place your own custom supports, custom G-code scripting, and even applying settings to different parts within the same print.
It has always been a great option for standalone use and brings profiles for dozens of 3D printers to use out of the box.
PrusaSlicer VS Orca Slicer: Summary of Pros And Cons
Here's the table converted to markdown format:
| PrusaSlicer | Orca Slicer | |
|---|---|---|
| Print Quality | High-quality prints with adjustable flow control | High-quality prints with mostly automatic settings |
| Custom Supports | Manual support placement gives more customization | Automated supports |
| Control | Advanced control over printing parameters | Allows advanced control but the slicer has useful automated control |
| Printer Compatibility | Wider 3D printer support | Works with Bambu Lab printers and many other printers |
| Preset Profiles | Many profiles for various printers | Offers profiles and downloadable support for printers |
| G-code Editing | Editable with complete control | Limited control (fewer custom variables) |
| Updates | Stable | Experimental updates |
| Open-source | Yes | A fork of BambuSlicer and open source |
| Common Users | Prusa printer users and professionals | Bambu Lab users and one-click print users |
Difference Between User Interface (UI)
Both Orca Slicer and PrusaSlicer have the same core UI, but Orca has upgraded and improved many usability features for workflow efficiency.
Prusa UI
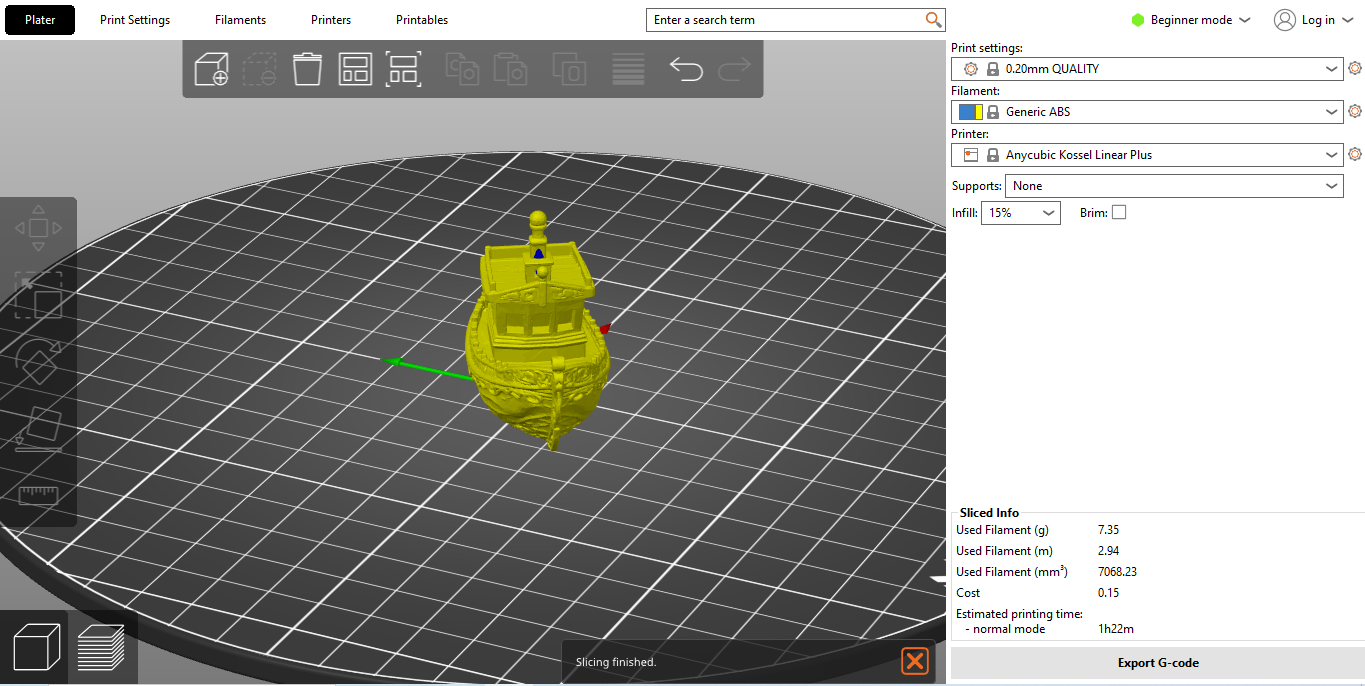
After installing PrusaSlicer, you’ll be asked to pick your view mode, from simple, advanced, and expert, during configuration. You can easily switch between modes in the slicer 3D viewer.
PrusaSlicer has a tabular view with panel settings and bottom controls. In the slicer window, the left toolbar has rotating and positioning tools, and most of the print settings are found grouped in the tabs on top.
PrusaSlicer has a logical organization for experienced users, but it can feel cluttered for beginners. Once you’ve changed your printing settings, the 3D viewer updates the print and you can see a preview of the supports, layers, and print position on the plate.
In the slicer view, you can also duplicate your prints, create instances and select individual objects to adjust parameters. You can easily rotate and adjust spacing between objects and paint on supports, which you can see in the 3D viewer as well.
Orca UI
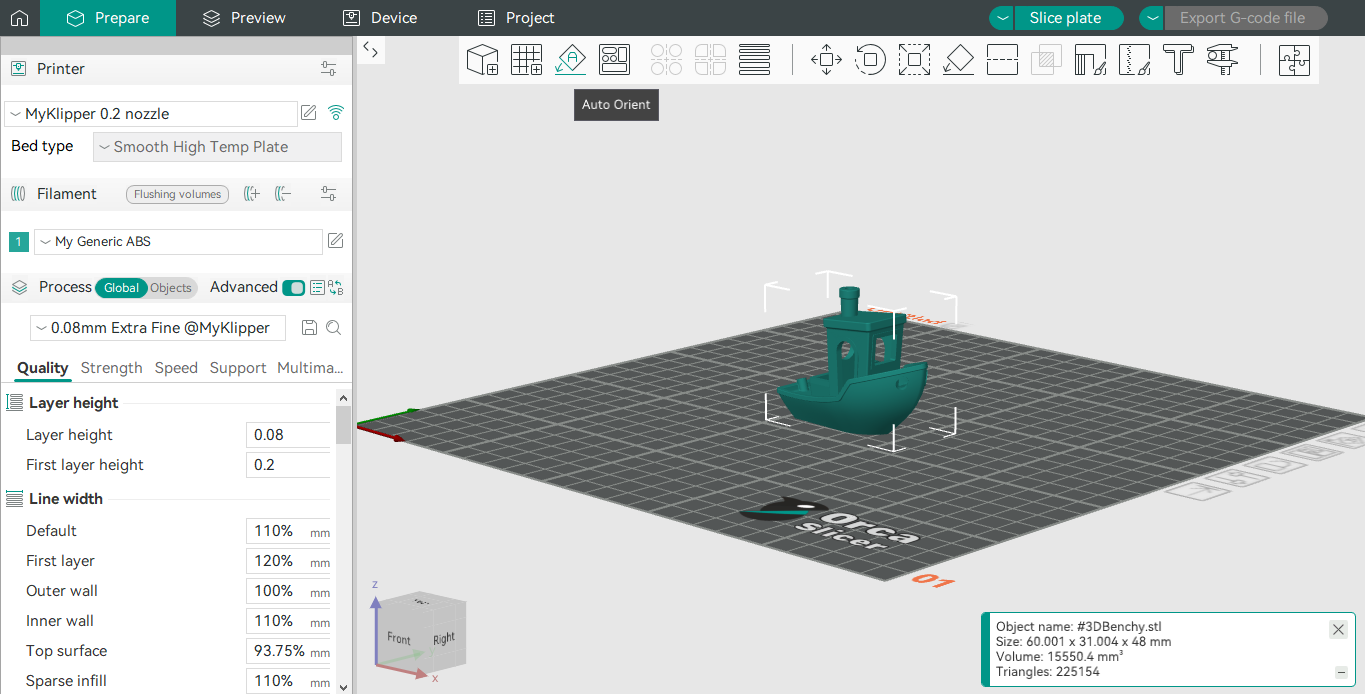
Orca has a much simpler user interface, in fact, the home screen simply has a button to import your model. Orca has many pre-installed profiles for printers, especially Bambu Lab printers which other slicers do not offer.
The slicer viewer has intuitive navigation tabs and most of the time you’ll only be using the prepare and preview tabs. On the left side bar, you’ll find all your printing parameters from nozzle choice to support raft settings. Most of the features will be hidden in the normal mode, but can be seen with a simple toggle switch.
Overview of layout:
- Left panel: print settings
- Right panel: 3D viewer & model adjuster (rotate, move and support)
- Top bar: Navigation and control
One great thing about Orca’s slicer is the print button turns green when all settings are acceptable.
Feature Comparison
PrusaSlicer is the original open source slicer, which has most of the traditional features and often offers more control over advanced features. Since v2.5 PrusaSlicer has perimeter generator, print simulation, and basic network printing capabilities.
Variable layer height
Both slicers offer variable layer height, ironing, infill adjustment and adaptive cubic infill.
Tree supports
Orca Slicer has advanced use of tree supports with automatic implementation. PrusaSlicer still relies on manual adjustments and implementation of tree supports.
Painting
You can paint on supports and seams in both slicers. Auto orientation Both slicers can auto-orient parts but Orca users report a better handling and adjustment of the model.
AI-based print failure detection
Orca offers a few AI features, but they are only available to Bambu Lab printers like failure detection. Network printing and remote control are available in printer profiles that support such features. Prusa has its network printing app called Prusa connect, which offers remote printing from anywhere.
Multiple Build Plates
In Orca you can manage multiple build plates within a single project. This lets you organize different parts on separate plates, each tailored with specific filament and profiles.
Common Features
- Variable width extrusion
- Auto-calibration
- Cubic infill
- Multi-material support
- Scripting
- Open-source
Performance Comparison
Orca Slicer is faster than PrusaSlicer for complex models mainly because the slicing engine is optimized for multi-core CPUs. It also has better memory management and utilizes the GPU more efficiently.
Orca also offers quicker previews and renders of model changes. Since the Orca v2.0 the performance has improved significantly with adaptive bed mesh support, pressure equalizer for smooth PLA extrusion, and Obico cloud integration.
Prusa utilizes lower RAM and is more efficient at handling large print files. The G-code files are more detailed and raw, allowing for edits, and it has faster start-up time.
On Bambu Lab forums and reddit, users report Orca Slicer tends to offer faster slicing times and efficient handling of complex prints with GPU acceleration and AI support generation.
Overall User Experience
Both slicers cater to different user preferences. Orca Slicer is more modern with many visible options from the get-go and more visual feedback in the 3D viewer. Prusa is more streamlined and has a traditional interface with a progressive learning curve from basic to advanced settings.
What’s noteworthy is the fact that Prusa has more stability which can be important for people who want uninterrupted printing with fewer crashes.
