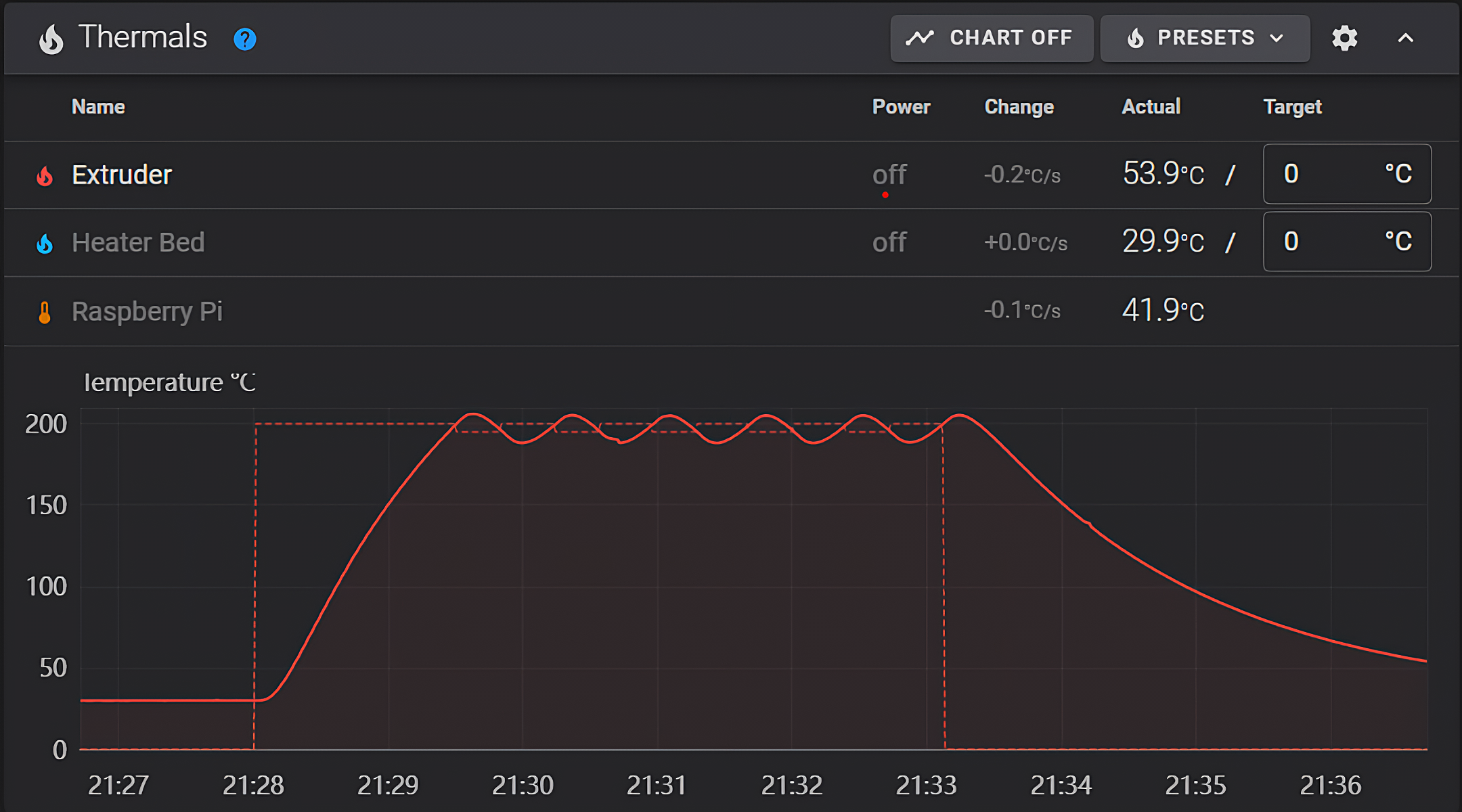
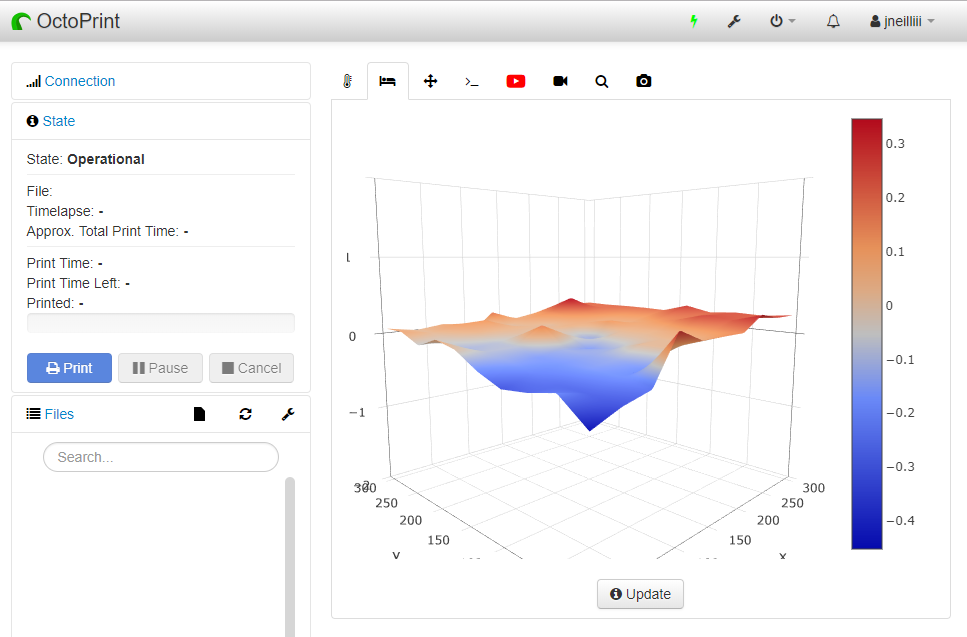
The core of 3D printing is a 3D model. 3D modeling for 3D printing is important as all 3D prints start with a digital CAD model that is "sliced" in a slicing software which the 3D printer prints. Being an integral part of 3D printing, having a working knowledge of 3D modeling and the various tools becomes crucial.
In this article, we'll go over the fundamentals of 3D modeling for 3D printing, as well as the distinction between inorganic and organic 3D models, and the popular software for each type.
We've included 3D modeling software for beginners for those on a low budget, as well as a few high-end options for professionals.
But first, to make sure we're all on the same page, let's go through the fundamentals of 3D printing.

A CAD design (left screen), slicing software (right), and the finished print / Courtesy: Ultimaker
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer using a computer-aided design, or CAD. 3D printing builds objects by layering materials such as polymers, composites, or biomaterials that vary in shape and size, as well as rigidity and color.
Even though 3D printing isn't new, there are some who will benefit from our guide to the most common 3D printing terms for beginners.
Regardless of the 3D printing technology being used, it all starts with a 3D CAD model. In this article, we will go through the fundamentals of 3D modeling and its different types, with a focus on 3D printing.
To further help you in selecting the best CAD software for your 3D models, we will also list out a number of 3D modeling software suitable for both beginner and advanced users.
So let's jump in!