Klipper Rotation Distance - All You Need to Know

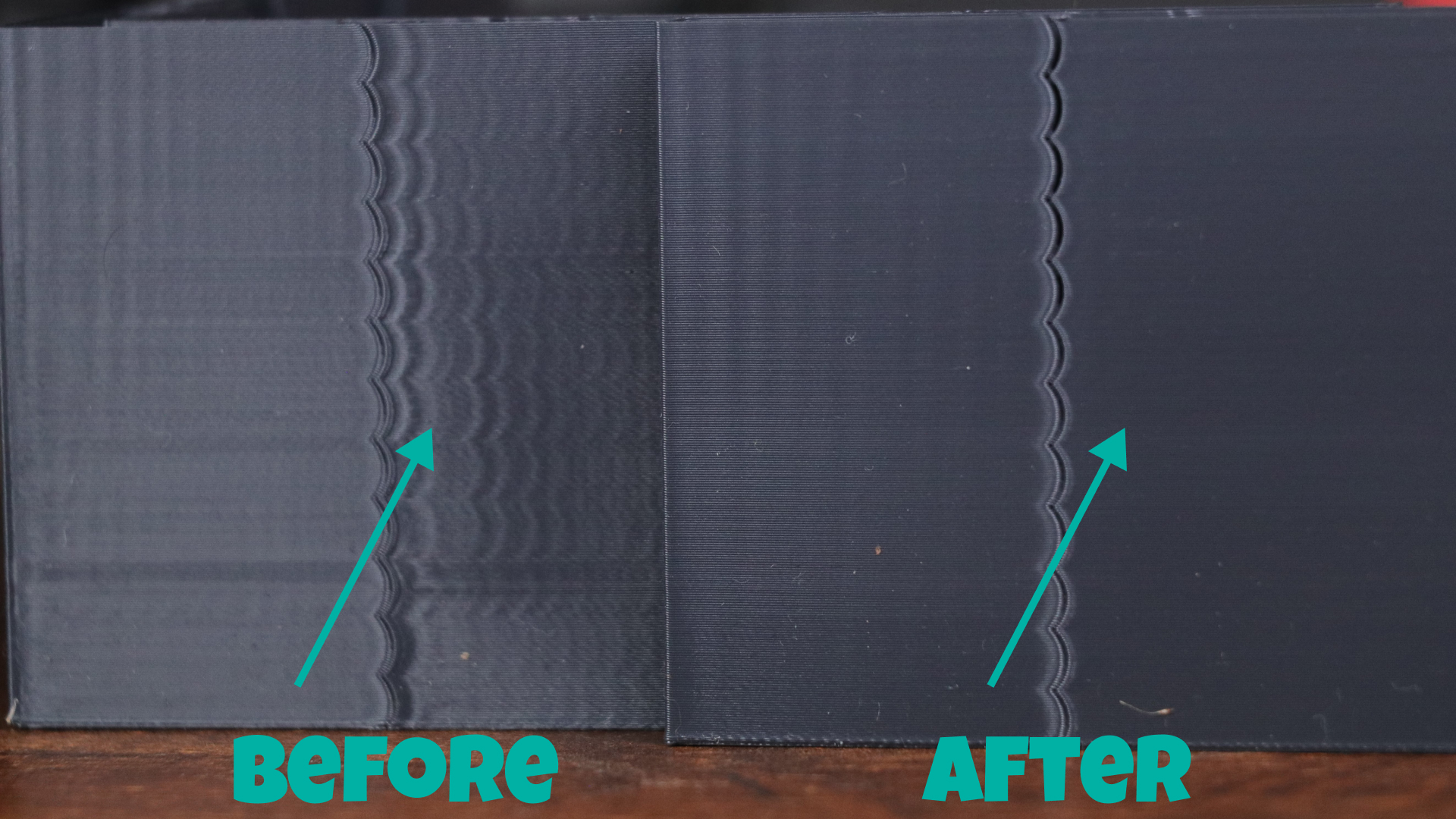
Photo Courtesy : 3D Printing Geek via Reddit
Klipper is an advanced 3D printing firmware that gives you a high level of control over how your 3D printer moves. One key part of this control is the measurement and management of your stepper motor's motion. Klipper does this with the help of the Rotation Distance parameter.
Rotation Distance measures how far your print head moves in a single rotation.This value has an impact on the dimensional accuracy and appearance of your prints. and, in turn, is a key factor in determining the final quality of your 3D models.
In this article, we'll talk about what the rotation distance means in Klipper and how you can use it to get the best prints possible. We'll talk about it in detail and go over the steps for setting up the rotation distance for your 3D printer.
Read on to learn how to 3D print highly accurate parts and take your printing to the next level.